
Claims Processing Software Development: Features, Benefits, and Implementation Guide
Is your organization still processing claims manually, drowning in paperwork, and losing revenue to errors and delays? You’re facing a challenge that costs the insurance industry billions annually. Manual claims processing leads to error rates as high as 25%, processing times stretching to weeks, and customer satisfaction scores that keep dropping.
According to Future Business Insights, the global claims management market size was valued at USD 4.60 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 5.15 billion in 2024 to USD 13.95 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 13.3% during the forecast period. North America dominated the global claims management market with a share of 45.65% in 2023.
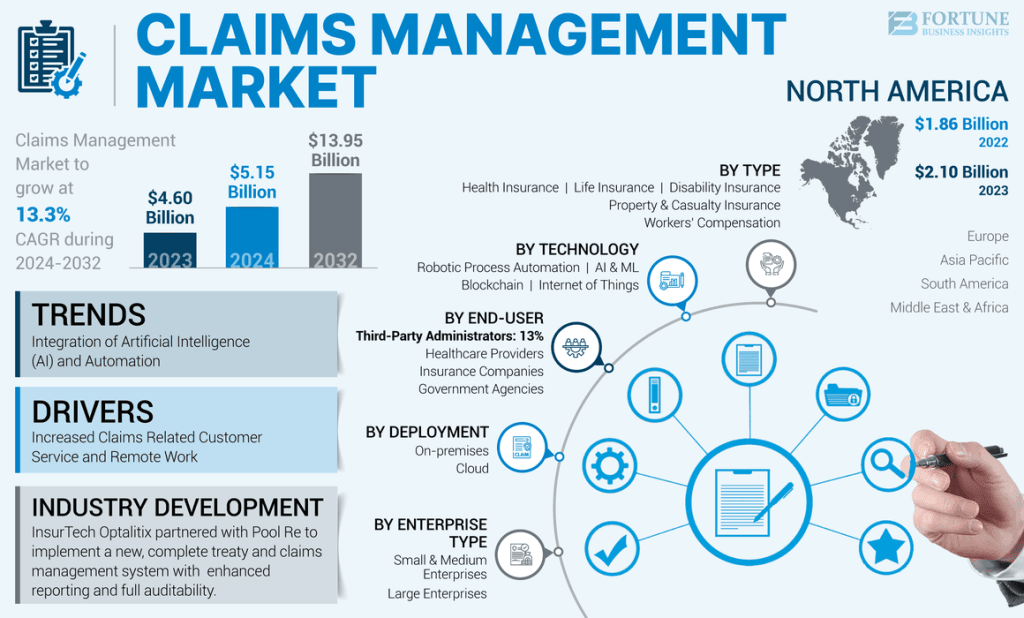
This rapid growth reflects how organizations across insurance, healthcare, and finance are prioritizing digital transformation to stay competitive.
Claims processing software development enables businesses to automate the entire claims lifecycle, from initial submission through adjudication to final payment. Organizations that partner with a healthcare software development company to build custom claims management solutions report reductions in processing time, lower operational costs, and faster, more accurate claim resolutions that significantly improve customer experiences.
This guide breaks down claims processing software development in practical terms. You’ll learn what features matter most, how development works, what it costs, and how to implement a system that transforms your claims operations.
What is Claims Processing Software?
Claims processing software is a digital platform that automates the management, evaluation, and settlement of claims across the insurance, healthcare, and financial services industries. Instead of manual paperwork shuffling between departments, these systems digitize the entire claims journey from submission to payment, ensuring faster resolutions and fewer errors.
At its core, claims processing software captures claim information, validates data against policy terms or coverage rules, routes claims through appropriate approval workflows, and triggers payments upon approval. Modern systems incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect fraud, predict outcomes, and continuously optimize processing efficiency.
Several industries rely heavily on claims processing software:
- Insurance: Property and casualty, auto, life, health, and specialty insurance
- Healthcare: Medical claims, pharmacy benefits, and patient reimbursements
- Finance: Warranty claims, dispute resolution, and chargeback management
- Government: Workers’ compensation, disability benefits, and social services
Organizations pursuing enterprise software development initiatives increasingly prioritize claims automation because of the measurable impact on operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Understanding claims processing fundamentals leads to the strategic question: Why should your organization invest in this technology?
Why Do Businesses Need Claims Processing Software?
The case for claims processing software goes beyond simple efficiency gains. Organizations face mounting pressure from rising claim volumes, increasing customer expectations for instant service, and regulatory requirements demanding detailed audit trails. Here are the six core reasons driving adoption.
1. Eliminate manual errors and reduce fraud
Manual claims processing introduces errors at every touchpoint. Data entry mistakes, misread documents, incorrect calculations, and overlooked policy exclusions cost organizations millions annually. Claims processing software validates information automatically against business rules, flags inconsistencies, and ensures accurate adjudication every time.
2. Accelerate claims processing time
Speed matters to claimants. Whether someone is waiting for a medical reimbursement or an insurance settlement after property damage, delays create frustration and erode trust. Manual processes that take weeks can be compressed to days or even hours with proper automation.
3. Improve customer satisfaction
Modern customers expect transparency and responsiveness. Claims processing software enables real-time status tracking, automated notifications, and self-service portals where claimants can submit documentation and check progress without calling customer service. This transparency transforms the claims experience from frustrating uncertainty to informed confidence.
4. Ensure regulatory compliance
Canadian organizations must comply with PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act) for data privacy, along with industry-specific regulations like provincial insurance acts. Healthcare organizations face additional requirements around health information protection. Claims processing software builds compliance into workflows automatically.
5. Reduce operational costs
Labour costs for manual claims handling are substantial. Each claim requires data entry, document review, adjudication, approval routing, payment processing, and customer communication. Automation handles routine tasks, reducing the cost per claim while improving throughput.
6. Enable data-driven decision making
Every claim generates valuable data. Claims processing software aggregates this information into dashboards and reports, revealing processing bottlenecks, fraud patterns, adjuster performance, and customer experience metrics. These insights drive continuous improvement. Identify which claim types take the longest to resolve. Spot emerging fraud schemes before they cause significant losses.
Pro Tip: Start your claims automation journey by documenting your current process flows and identifying the highest-volume, most repetitive tasks. These represent the quickest wins for automation and build momentum for broader transformation.
With the business case established, let’s examine the specific capabilities that make claims processing software effective.
What are the Key Features of Claims Processing Software?
Effective claims processing software combines multiple capabilities into a unified platform. While specific features vary based on industry and organizational needs, these ten capabilities form the foundation of comprehensive claims management.
1. Automated claims intake and validation
The claims journey begins with intake. Modern systems accept claims through multiple channels: web portals, mobile apps, email, electronic data interchange (EDI), and even traditional mail through document scanning. Automated validation checks submissions for completeness, verifies claimant identity, and confirms coverage eligibility before claims enter the processing queue.
2. Document management and OCR integration
Claims generate substantial documentation: medical records, police reports, repair estimates, photographs, receipts, and correspondence. Document management features organize these materials, link them to appropriate claims, and enable full-text search across the entire document repository. Optical character recognition (OCR) extracts data from scanned documents and images, eliminating manual data entry.
3. Workflow automation and routing
Different claims require different handling. A straightforward auto glass claim follows a simpler path than a complex liability dispute. Workflow engines route claims based on type, complexity, value, and other criteria, ensuring each claim reaches the appropriate adjuster or approval authority. Automated workflows also manage escalations, deadline monitoring, and handoffs between departments.
4. Real-time claims tracking and status updates
Claimants and internal stakeholders need visibility into claim progress. Real-time tracking shows exactly where each claim stands in the process, what actions are pending, and expected resolution timelines. Automated notifications keep everyone informed without manual outreach. Email or SMS updates confirm receipt, request additional documentation, communicate decisions, and provide payment confirmation.
5. Fraud detection and prevention
Fraudulent claims drain organizational resources and increase costs for legitimate customers. Claims processing software incorporates multiple fraud prevention mechanisms. Rule-based detection flags claims matching known fraud patterns: duplicate submissions, provider billing anomalies, or suspicious timing. Organizations investing in AI development services can implement sophisticated fraud detection that continuously learns and adapts.
6. Compliance management tools
Regulatory requirements demand systematic compliance management. Built-in tools ensure proper consent collection, data handling, retention periods, and audit trail maintenance. For organizations handling healthcare software development projects, compliance features must address PIPEDA, provincial health information acts, and potentially HIPAA for cross-border operations.
Build Claims Processing Software That Reduces Rework and Delays
Design a claims processing system that validates data at submission, minimizes manual corrections, and improves first-pass acceptance across payers.
Understanding features clarifies what’s possible. Now let’s examine the different types of claims processing software serving various industries.
What are the Different Types of Claims Processing Software?
Claims processing requirements vary significantly across industries. While core automation principles apply universally, specialized solutions address unique workflows, compliance requirements, and integration needs for different sectors.
1. Healthcare claims processing software
Healthcare claims involve complex interactions between patients, providers, payers, and regulators. Medical claims processing software handles eligibility verification, procedure coding (ICD-10, CPT), benefit calculation, and coordination between multiple insurance coverages.
Key requirements include:
- HIPAA and PIPEDA compliance for protected health information
- EDI transaction processing using standard formats (837, 835, 270/271)
- Provider credentialing verification and network management
- Medical necessity review and prior authorization workflows
- Integration with EHR systems for clinical documentation
Organizations developing healthcare claims solutions should explore EHR software development best practices to ensure seamless clinical integration.
2. Insurance claims processing software
Property and casualty, auto, life, and specialty insurers each have distinct claims workflows. Insurance claims management systems handle policy verification, coverage determination, reserve establishment, loss adjustment, and settlement processing. Organizations investing in scalable claims platforms often partner with specialists offering insurance software development services to ensure regulatory alignment, system scalability, and long-term operational efficiency.
Auto insurance claims might include:
- Damage assessment through photos or virtual inspection
- Repair network management and direct repair programs
- Subrogation tracking for recovery from at-fault parties
- Total loss evaluation and salvage disposition
Property claims address:
- Catastrophe management for high-volume events
- Contents inventory and valuation
- Contractor management for repairs
- Business interruption calculations
3. Warranty claims management software
Manufacturers and retailers process warranty claims differently than insurers. Warranty systems track product registration, validate warranty coverage, authorize repairs or replacements, and manage parts logistics.
Important capabilities include:
- Product serial number tracking and registration
- Failure analysis and quality feedback loops
- Parts ordering and inventory management
- Service network coordination
- Customer communication throughout resolution
4. Workers’ compensation claims software
Workers’ compensation combines elements of insurance claims and healthcare management. These systems track workplace injuries, manage medical treatment authorization, calculate disability payments, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Specialized features include:
- Injury reporting and OSHA compliance
- Return-to-work programs and accommodation tracking
- Medical bill review and fee schedule compliance
- Litigation management for disputed claims
- Experience modification calculations
Each claims type presents unique development considerations. The next section explains how these systems actually process claims from submission to resolution.
How Does Claims Processing Software Work?
Claims processing software orchestrates a complex workflow involving data capture, validation, decision-making, and payment execution. Understanding this process helps organizations identify automation opportunities and set realistic expectations for system implementation.
Step 1: Claims submission
The process begins when a claimant reports a loss or requests reimbursement. Modern systems accept submissions through web portals, mobile apps, API integrations, EDI transactions, email parsing, and call centres. Regardless of channel, all submissions flow into a unified intake queue for processing.
Step 2: Data capture and validation
Raw submissions undergo immediate validation, including claimant identity verification, coverage eligibility checks, completeness review, duplicate detection, and basic fraud screening. OCR and intelligent document processing extract information from uploaded documents, reducing manual data entry and accelerating downstream processing.
Step 3: Automated adjudication
Many claims can be adjudicated automatically against business rules covering policy terms, coverage limits, deductibles, exclusions, and benefit calculations. Claims meeting straight-through processing criteria receive automatic approval and proceed to payment, while complex claims requiring human judgment route to appropriate adjusters.
Step 4: Review and approval workflow
Claims requiring manual review enter structured workflows where adjusters receive prioritized queues with all relevant information. Investigation may include document review, third-party verification, field inspections, medical reviews, and fraud investigations. Workflow engines track tasks, manage escalations, and route claims through approval hierarchies.
Step 5: Payment processing
Approved claims trigger payment execution through multiple methods including electronic funds transfer, cheque generation, provider network payments, and payment cards. Processing includes proper tax reporting, accounting integration, and reconciliation support to ensure accurate financial management.
Step 6: Reporting and analytics
Throughout the claims lifecycle, systems capture metrics enabling operational analysis. Reporting capabilities transform this data into actionable intelligence for management review and continuous improvement initiatives.
[Insert infographic: Claims Processing Workflow Diagram]
Image name: claims-processing-workflow-diagram.png
Alt text: Claims processing software workflow showing six steps from submission through payment and reporting
With the process clarified, let’s explore why organizations choose custom development over off-the-shelf solutions.
What are the Benefits of Custom Claims Processing Software Development?
Organizations evaluating claims processing solutions face a fundamental choice: implement packaged software or build custom systems. While commercial platforms offer faster initial deployment, custom development delivers advantages that matter for organizations with unique requirements or competitive differentiation goals.
1. Tailored to your specific business workflows
Every organization processes claims differently. Unique product structures, underwriting philosophies, customer service approaches, and operational procedures create workflows that packaged software can’t perfectly accommodate.
Custom development builds software around your processes rather than forcing process changes to fit software limitations. Your claims system works the way your business works.
2. Seamless integration with existing systems
Enterprise environments include policy administration systems, customer databases, accounting platforms, and reporting tools accumulated over years. Custom development enables deep integration with these existing investments.
Rather than maintaining separate data silos or relying on clunky middleware, custom systems share information seamlessly across your technology ecosystem.
3. Scalability as your business grows
Business growth brings changing requirements. Entering new markets, launching new products, or acquiring competitors introduces complexity that packaged software may not accommodate.
Custom systems scale architecturally to handle increased volume and functionally to support new business requirements. You’re not constrained by vendor roadmaps or waiting for features that may never arrive.
4. Full ownership and control
Custom development means you own the code. No licensing fees that increase annually. No vendor lock-in limiting your options. No dependency on external roadmaps for critical functionality.
This ownership provides flexibility for future modifications, potential licensing to partners, and protection against vendor business changes.
5. Competitive advantage through unique features
Claims experience increasingly differentiates insurers and healthcare organizations. Custom development enables unique capabilities competitors using packaged software can’t match.
Innovative self-service features, proprietary fraud detection algorithms, or distinctive customer communication approaches become possible when you control the development roadmap.
6. Long-term cost savings
While custom development requires larger upfront investment, total cost of ownership often favours custom solutions for organizations with significant claims volume. Eliminating per-claim fees, avoiding annual licensing increases, and reducing customization costs for packaged platforms accumulate substantial savings over time.
Replace Fragmented Claims Workflows With a Unified Platform
Create claims processing software that connects eligibility checks, coding, submissions, denials, and follow-ups into one streamlined system.
Understanding benefits prepares you for the development journey. Here’s a systematic approach to building claims processing software.
How to Develop Claims Processing Software: Step-by-Step Guide
Building effective claims processing software requires methodical planning, skilled execution, and ongoing refinement. This step-by-step guide outlines the development process from initial concept through deployment and maintenance.
Step 1: Define business requirements and objectives
Successful development starts with clear requirements. Document your current claims processes, identify pain points, and establish measurable objectives for the new system.
Key questions to answer:
- What claim types will the system handle?
- What are current processing volumes and growth projections?
- Which existing systems require integration?
- What compliance requirements apply?
- What are the target metrics for processing time, accuracy, and cost?
Involve claims adjusters, customer service representatives, compliance officers, and IT stakeholders in requirements gathering. Healthcare organizations can also align this phase with a proven EHR development process to ensure clinical data, billing workflows, and compliance needs are accurately reflected from the start. Their frontline experience reveals requirements that management perspectives might miss.
Step 2: Choose the right technology stack
Technology decisions impact development speed, system performance, maintenance costs, and long-term flexibility. Consider:
- Scalability requirements for peak volume handling
- Integration capabilities with existing enterprise systems
- Security features for sensitive claims data
- Developer availability for ongoing maintenance
- Cloud versus on-premise deployment preferences
The following section details specific technology recommendations for claims processing development.
Step 3: Design intuitive UI/UX
Claims processing involves multiple user types with different needs. Adjusters need efficient workflows for high-volume processing. Managers need dashboards for oversight. Claimants need simple, reassuring interfaces for submissions and status checking.
User experience design should prioritize:
- Efficiency for power users processing many claims daily
- Clarity for occasional users navigating unfamiliar processes
- Accessibility meeting WCAG standards for users with disabilities
- Mobile responsiveness for field and on-the-go access
Step 4: Develop core features and integrations
Development typically proceeds in phases, starting with core claims intake and processing capabilities before adding advanced features. Many healthcare organizations adopt a phased rollout similar to EHR MVP development—launching essential claims functionality early, validating workflows, and scaling capabilities based on real user feedback. An agile approach delivers working functionality incrementally, enabling early feedback and course correction.
Organizations following agile software development methodologies benefit from regular sprint deliveries that build momentum and maintain stakeholder engagement throughout the project.
Integration development often parallels core feature work. Early integration with policy systems, customer databases, and payment platforms ensures the claims system operates within the broader enterprise ecosystem.
Step 5: Implement security and compliance measures
Claims data includes sensitive personal and financial information requiring robust protection. Security implementation includes:
- Encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Access controls with role-based permissions
- Audit logging for compliance documentation
- Penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities
- Disaster recovery planning and implementation
Canadian organizations must ensure PIPEDA compliance, with additional requirements for healthcare claims under provincial health information acts.
Step 6: Test thoroughly
Comprehensive testing validates system functionality, performance, and security before production deployment.
Testing types include:
- Unit testing for individual components
- Integration testing for system interactions
- User acceptance testing with actual claims scenarios
- Performance testing under expected and peak loads
- Security testing including vulnerability assessment
Test with realistic data volumes and scenarios. Edge cases that seem unlikely during development often appear regularly in production.
Step 7: Deploy and train users
Deployment planning addresses technical infrastructure, data migration, and user transition. Consider phased rollouts that limit risk by introducing the new system to subset of users or claim types before full deployment.
Training ensures users can leverage system capabilities effectively. Role-specific training addresses different user needs:
- Adjusters: Efficient claim processing workflows
- Managers: Reporting and oversight capabilities
- Customer service: Claimant inquiry handling
- IT staff: Administration and troubleshooting
Step 8: Maintain and iterate
Deployment marks the beginning, not the end, of the software lifecycle. Ongoing maintenance addresses:
- Bug fixes for issues discovered in production
- Security updates responding to emerging threats
- Performance optimization as volumes grow
- Feature enhancements based on user feedback
- Regulatory updates for compliance changes
Quick Tip: Plan for a parallel processing period where both old and new systems operate simultaneously. This provides fallback capability and allows direct comparison of processing results before fully retiring legacy systems.
With dethe velopment approach established, let’s examine the cost of developing a claim processing software.
How Much Does Claims Processing Software Development Cost?
Developing an insurance claims processing app typically costs between $50,000 and $500,000 or more, depending on whether you choose a basic solution, a feature-rich complex system, or a full enterprise-grade platform.
Well, development costs vary significantly based on system complexity, feature requirements, and implementation approach. Understanding cost drivers helps organizations budget appropriately and evaluate proposals effectively.
1. Factors affecting development cost
Several variables influence total project investment:
- Complexity and feature scope: Basic claims intake and processing costs less than comprehensive systems with AI fraud detection, multiple integration points, and advanced analytics.
- Integration requirements: Connecting with existing enterprise systems, external data sources, and industry networks adds development effort and cost.
- Compliance requirements: Healthcare claims requiring HIPAA compliance or insurance systems needing regulatory reporting add specialized development and testing effort.
- User interface sophistication: Simple administrative interfaces cost less than polished customer-facing portals with mobile apps.
- Team composition: Senior developers with claims domain expertise command higher rates but deliver faster, higher-quality results.
- Timeline pressure: Accelerated timelines require larger teams or overtime, increasing costs.
2. Cost estimates by complexity level
These estimates assume development with an experienced partner. In-house development with newly hired teams typically costs more due to learning curves and recruitment expenses.
3. Ongoing costs to consider
Beyond initial development, budget for:
- Hosting and infrastructure: Cloud services, databases, storage
- Maintenance and support: Bug fixes, security updates, performance optimization
- Enhancements: New features and capability additions
- Compliance updates: Regulatory change implementation
Important Note: The lowest quote isn’t always the best value. Experienced developers who understand claims processing deliver faster, build more maintainable systems, and avoid costly mistakes that less experienced teams make. Evaluate total value, not just hourly rates.
Cost clarity supports planning. Now let’s address the challenges you’ll encounter and how to overcome them.
What are the Challenges in Claims Processing Software Development? [Ways to Overcome Them]
Claims processing software development presents unique challenges beyond typical enterprise software projects. Anticipating these obstacles enables proactive planning and successful navigation.
1. Data security and privacy concerns
Claims data includes sensitive personal information, financial details, and health records. Breaches expose organizations to regulatory penalties, litigation, and reputational damage.
Solution: Implement security from the architecture level, not as an afterthought. Encrypt sensitive data, enforce least-privilege access controls, maintain comprehensive audit logs, and conduct regular security assessments. Canadian organizations must specifically address PIPEDA requirements, with additional protections for healthcare claims under provincial health information acts.
2. Integration with legacy systems
Many organizations operate claims-related systems built decades ago on obsolete technologies. In healthcare environments, EHR modernization becomes essential to improve data accessibility, system interoperability, and real-time claims processing efficiency without disrupting clinical operations. These systems contain critical data and business logic but lack modern integration capabilities.
Solution: Develop robust integration layers that bridge legacy and modern systems. API gateways, middleware, and data transformation services can connect disparate systems without requiring immediate legacy replacement. Plan for eventual modernization while enabling current interoperability.
3. Regulatory compliance complexity
Claims processing touches multiple regulatory domains: privacy, insurance, healthcare, financial services. Requirements vary by jurisdiction and change frequently.
Solution: Build compliance into system design rather than bolting it on later. Maintain configuration-driven compliance rules that can be updated without code changes. Establish relationships with legal and compliance experts who can interpret requirements for technical implementation.
4. User adoption resistance
Claims adjusters and customer service representatives may resist new systems, especially if they perceive technology as threatening their jobs or complicating their work.
Solution: Involve end users throughout development. Gather their input on requirements, demonstrate prototypes for feedback, and incorporate their suggestions. Position automation as handling tedious work so they can focus on complex claims requiring human judgment. Comprehensive training and support ease the transition.
5. Scalability requirements
Claims volumes fluctuate dramatically. Catastrophic events like natural disasters can multiply normal volumes tenfold within hours. Systems must handle these spikes without degradation.
Solution: Design for elastic scalability from the start. Cloud infrastructure enables rapid resource expansion during peak periods. Asynchronous processing queues handle volume bursts without overwhelming downstream systems. Load testing validates performance under realistic peak scenarios.
Pro Tip: Create a disaster response plan that addresses both business continuity and system scalability. When catastrophe strikes, you’ll need a rapid scaling capability and clear procedures for prioritizing claims processing.
Understanding challenges prepares you for reality. Looking forward, emerging technologies promise even greater capabilities.
What is the Future of Claims Processing Software?
Claims processing technology continues to evolve rapidly. Understanding emerging trends helps organizations plan investments that remain relevant as capabilities advance.
1. AI and machine learning for intelligent claims adjudication
Artificial intelligence already enhances fraud detection and decision support. Future systems will handle increasingly complex adjudication automatically, learning from adjuster decisions to replicate human judgment at scale.
Natural language processing will extract information from unstructured documents, medical records, and communications. Computer vision will assess damage from photos and videos with accuracy matching human experts.
2. Blockchain for transparent and secure claims tracking
Blockchain technology offers immutable record-keeping and transparent transactions. For claims processing, this enables:
- Verifiable claim histories that can’t be altered
- Smart contracts automate payments upon verified conditions
- Consortium networks sharing fraud information across organizations
- Subrogation automation between insurers
Early implementations demonstrate potential, though widespread adoption awaits industry standardization.
3. IoT integration for real-time data collection
Internet of Things devices generate continuous data streams relevant to claims. Connected vehicles report accidents automatically. Smart home sensors detect water leaks before they cause major damage. Wearables monitor health conditions for life and disability insurance.
Claims systems integrating IoT data can:
- Verify claim circumstances with objective sensor data
- Enable parametric insurance to pay automatically when conditions occur
- Support proactive intervention, preventing claims through early warning
4. Natural language processing for document analysis
Unstructured text in claims documents, correspondence, and medical records contains valuable information currently requiring manual review. Advanced NLP capabilities will:
- Extract key facts from lengthy documents automatically
- Summarize medical records for adjuster review
- Analyze correspondence sentiment for customer experience insights
- Identify relevant precedents from historical claims
5. Predictive analytics for fraud prevention and claims forecasting
Moving beyond reactive fraud detection, predictive analytics anticipates fraudulent schemes before they cause significant losses. Pattern recognition across industry data identifies emerging tactics.
Claims forecasting helps organizations prepare for volume fluctuations, staffing requirements, and reserve adequacy. Weather-correlated models predict property claim surges. Economic indicators forecast disability claim trends.
Organizations building for the future should partner with development teams experienced in artificial intelligence software development to incorporate emerging capabilities effectively.
Develop Compliance-Ready Claims Processing Software With Space-O
Partner with Space-O to build secure claims systems that align with payer policies, audit standards, and healthcare regulatory requirements.
The future is bright for claims processing technology. Now, let’s discuss how Space-O Technologies can help you capitalize on these opportunities.
Partner with Space-O Technologies for Reliable Claims Processing Software
Choosing the right development partner plays a critical role in the success of claims processing software. Space-O Technologies combines deep technical expertise with a strong understanding of healthcare, insurance, and financial services workflows to deliver reliable, high-performance solutions.
Since 2018, we have been supporting organizations throughout the entire development lifecycle, from planning to long-term optimization. Our strong presence in the Canadian market allows us to build claims processing systems that meet PIPEDA requirements and provincial healthcare regulations.
We also leverage AI and machine learning to enable intelligent automation, fraud detection, and predictive analytics, while ensuring seamless integration with EHR platforms, payment systems, and legacy infrastructure.
Through agile development, dedicated teams, and ongoing post-launch support, Space-O Technologies remains focused on delivering secure, compliant, and scalable claims processing software that drives lasting business value. Ready to transform your claims processing operations? Schedule a Free Consultation to discuss your requirements with our team.
Frequently Asked Questions About Claims Processing Software
How long does it take to develop claims processing software?
Development timelines vary by complexity. Basic claims processing systems typically require 3-4 months. Medium complexity solutions with integrations and advanced features take 4-6 months. Complex enterprise systems with AI capabilities and multiple integrations may require 6-12 months or longer.
How much does claims processing software development cost?
Costs range from $50,000-$80,000 for basic systems to $300,000+ for comprehensive enterprise solutions. Key factors include feature scope, integration requirements, compliance needs, and timeline. Contact Space-O Technologies for a detailed estimate based on your specific requirements.
Can claims processing software integrate with existing systems?
Yes. Modern claims processing software is designed for integration with policy administration systems, CRM platforms, EHR systems, payment processors, and legacy applications. API-based architecture enables connection with virtually any system that supports standard integration methods.
What industries benefit from claims processing software?
Multiple industries use claims processing software, including health insurance, property and casualty insurance, life insurance, auto insurance, healthcare providers, manufacturers (warranty claims), government agencies (workers’ compensation, benefits), and financial services (dispute resolution).
Is claims processing software PIPEDA and HIPAA compliant?
Claims processing software can be developed to meet PIPEDA, HIPAA, and other regulatory requirements. Compliance features include data encryption, access controls, audit logging, consent management, and data residency controls. Space-O Technologies builds compliance into system architecture from the start.
What technologies are used in claims processing software development?
Modern claims processing systems typically use React, Angular, or Vue.js for frontend interfaces; Python, Java, Node.js, or .NET for backend processing; PostgreSQL or MongoDB for databases; TensorFlow or PyTorch for AI/ML capabilities; and AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for hosting infrastructure.
What is straight-through processing in claims?
Straight-through processing (STP) refers to claims that flow from submission through payment without human intervention. Automated validation, adjudication, and payment processing handle routine claims meeting predefined criteria, freeing adjusters to focus on complex cases requiring judgment.
How do I choose between building custom software and buying packaged solutions?
Consider custom development if you have unique workflows, require deep integration with existing systems, want competitive differentiation through distinctive capabilities, or anticipate significant customization of packaged software. Packaged solutions may suit organizations with standard processes, limited budgets, or urgent timelines. Space-O Technologies can help evaluate your specific situation.

Develop Compliance-Ready Claims Processing Software With Space-O
All our projects are secured by NDA
100% Secure. Zero Spam
*All your data will remain strictly confidential.
Trusted by


Bashar Anabtawi
Canada
“I was mostly happy with the high level of experience and professionalism of the various teams that worked on my project. Not only they clearly understood my exact technical requirements but even suggested better ways in doing them. The Communication tools that were used were excellent and easy. And finally and most importantly, the interaction, follow up and support from the top management was great. Space-O not delivered a high quality product but exceeded my expectations! I would definitely hire them again for future jobs!”

Canada Office
2 County Court Blvd., Suite 400,
Brampton, Ontario L6W 3W8
Phone: +1 (602) 737-0187
Email: sales@spaceo.ca

