
The Complete Guide to Software Development Project Planning
Software development projects face significant challenges, with industry research showing that a majority struggle to meet their original scope, timeline, or budget objectives. As per McKinsey, research indicates that large IT projects run 45% over budget and 7% over time, while delivering 56% less value than predicted.
If you’re managing a development project, you’re aware of the challenge: creating a software development project plan that balances stakeholder expectations, technical requirements, and evolving methodologies—while keeping everything on track. A well-structured plan acts as the blueprint for execution, helping align teams, manage risks, and measure progress toward successful delivery.
The difference between success and failure often comes down to one critical factor: your project plan. As a trusted software development company, Space-O Technologies has delivered over 300 successful software projects by following proven software development methodologies.
Our comprehensive guide provides the exact framework you need, from creating your initial plan to avoiding costly mistakes that derail even well-funded projects. Let’s understand why do you need a plan
Why Do You Need a Software Development Project Plan?
A well-defined software development project plan is critical to delivering your product on time, within budget, and according to business goals. Without a clear plan, even experienced teams risk miscommunication, missed deadlines, and spiraling costs.
Here’s exactly why it matters:
- Defines What You’re Building: It outlines core features, technical requirements, and business objectives—so your team isn’t guessing what to deliver or prioritizing the wrong tasks.
- Prevents Scope Creep: By setting clear boundaries on what’s in scope (and what’s not), the plan keeps “just one more feature” from derailing your timeline or budget.
- Aligns All Stakeholders: From product owners and developers to QA testers and clients, everyone understands their roles, deadlines, and what success looks like.
- Improves Resource Allocation: Helps assign the right people to the right tasks, forecast developer workloads, and avoid last-minute hiring or burnout.
- Minimizes Delays and Risks: Identifies potential risks—like unclear requirements, third-party dependencies, or integration challenges—before they impact delivery.
- Controls Budget: Provides cost estimates tied to deliverables and timelines, making it easier to stay within budget and justify spend to stakeholders.
- Tracks Progress and Quality: Defines measurable milestones, KPIs, and review points, so you can monitor progress, catch issues early, and maintain quality standards throughout development.
In short, a project plan is your execution roadmap—turning a software idea into a structured, successful delivery.
Let’s cut to the chase and jump straight to the step-by-step process.
10-Step Process to Create a Software Development Project Plan
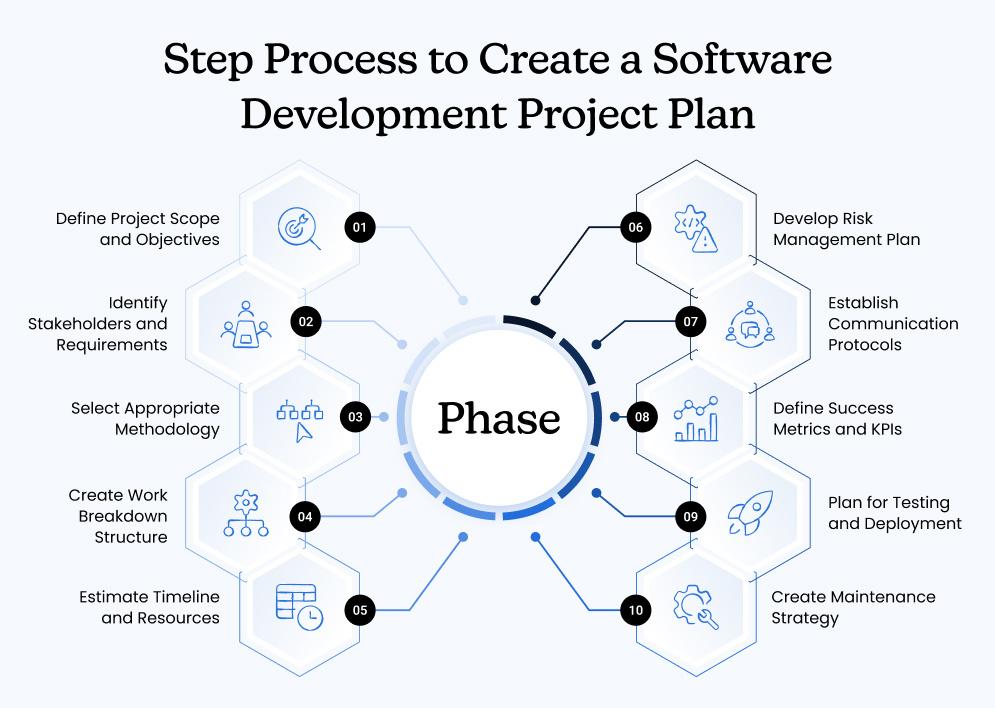
Creating a software development project plan doesn’t have to be overwhelming. This 10-step framework helps break down the entire software development process into manageable phases:
| Step | Phase | Key Deliverables | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Define Project Scope and Objectives | Project charter, problem statement, business case, defined project goals, scope boundaries, out-of-scope items | 2-3 days |
| 2 | Identify Stakeholders and Requirements | Stakeholder matrix, user personas, requirement gathering interviews, MoSCoW prioritization, functional & non-functional requirements documentation | 1 week |
| 3 | Select Appropriate Methodology | Chosen methodology (e.g., Agile, Scrum, Waterfall), rationale for selection, sprint plan or phase breakdown, process flow diagrams | 1-2 days |
| 4 | Create Work Breakdown Structure | WBS chart, task breakdown in tools like Jira/Trello, Gantt chart, task dependency mapping | 3-4 days |
| 5 | Estimate Timeline and Resources | Project timeline with milestones, resource allocation matrix, capacity planning sheet, team assignments, buffer time estimates | 1 week |
| 6 | Develop Risk Management Plan | Risk register with probability and impact scores, mitigation & contingency plans, risk ownership chart | 2-3 days |
| 7 | Establish Communication Protocols | Communication matrix, meeting cadence (daily standups, sprint reviews), reporting templates, stakeholder reporting schedule | 1 day |
| 8 | Define Success Metrics and KPIs | Defined KPIs (e.g., velocity, defect density, customer satisfaction), metric dashboards (Jira/Power BI), success/failure criteria | 2 days |
| 9 | Plan for Testing and Deployment | QA strategy document, test cases (unit, integration, UAT), deployment checklist, rollback plan, staging vs production environment setup | 3-4 days |
| 10 | Create Maintenance Strategy | Post-launch support plan (SLA, support levels), incident response process, technical documentation, knowledge base or helpdesk setup | 2 days |
Let’s look at each step up close; you will be creating effective and optimized project plans in no time after going through these steps one by one.
Step 1: Define project scope and objectives
Start by clearly defining what your software will achieve. Document the business problem you’re solving, specific features to be developed, and what’s explicitly out of scope. Create a project charter that includes your vision statement, core objectives, and success criteria.
For example, “Develop a mobile inventory management system that reduces stock counting time by 50% within 6 months” provides clear, measurable goals.
Step 2: Identify stakeholders and requirements
Map out everyone who will impact or be impacted by your project. Create a stakeholder matrix identifying sponsors, end users, development team members, and support staff. Gather requirements through interviews, surveys, and workshops.
Document both functional requirements (what the software does) and non-functional requirements (performance, security, usability standards). Use tools like user stories or use cases to capture requirements from the end-user perspective.
Step 3: Select appropriate methodology
Choose between Agile, Waterfall, or Hybrid approaches based on your project characteristics. Select Agile for projects with evolving requirements and frequent stakeholder feedback needs. Choose Waterfall when requirements are fixed and regulatory compliance demands extensive documentation.
Opt for the Hybrid approach when you need Waterfall’s structure for infrastructure components but Agile’s flexibility for user-facing features. Document your choice and ensure all team members understand the selected approach.
To understand which model aligns best with your project, it’s helpful to compare the Agile vs. Waterfall methodologies in terms of structure, flexibility, stakeholder involvement, and risk tolerance.
Step 4: Create work breakdown structure (WBS)
Break your project into smaller, manageable components. Start with major deliverables, then decompose each into specific tasks.
For a typical web application, your WBS might include:
- Backend Development (API design, database schema, authentication)
- Frontend Development (UI components, user flows, responsive design)
- Infrastructure (hosting setup, CI/CD pipeline, monitoring)
Each task should be small enough to estimate accurately, often in the range of 8-40 hours of work, though this varies by team and project type.
Step 5: Estimate timeline and resources
Use multiple software development estimation techniques for accuracy. Apply three-point estimation (optimistic, pessimistic, most likely) for uncertain tasks. Conduct Planning Poker sessions with your team to leverage collective experience.
Consider adding a 20-30% buffer time for unexpected complexities, adjusting based on project risk and complexity. Calculate resource needs based on skill requirements and availability.
Remember Hofstadter’s Law: Projects always take longer than expected, even when accounting for Hofstadter’s Law.
Step 6: Develop risk management plan
Identify potential risk in software development using techniques like SWOT analysis or risk brainstorming sessions. Categorize risks by probability and impact. High-probability, high-impact risks might include key developer turnover or third-party API changes.
Create mitigation strategies for each significant risk. Establish trigger points that activate contingency plans. Assign risk owners responsible for monitoring and responding to specific risks.
Step 7: Establish communication protocols
Define how information flows throughout your project. Specify meeting cadences (daily standups, weekly stakeholder updates, monthly steering committees), reporting formats, and escalation paths.
Create a RACI matrix that establishes who’s Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each project element. Document preferred communication channels, such as Slack for quick questions, email for formal decisions, and video calls for complex discussions.
Step 8: Define success metrics and kpis
Establish measurable indicators of project health and success. Technical metrics might include code coverage (aim for 80%+), deployment frequency, and defect rates.
Business metrics could encompass user adoption rates, performance improvements, or cost savings.
Set up dashboards to track these metrics throughout development. Define acceptable thresholds and what actions to take when metrics fall outside target ranges.
Step 9: Plan for testing and deployment
Develop a comprehensive testing strategy covering unit tests, integration tests, user acceptance testing, and performance testing. Define test scenarios, acceptance criteria, and bug severity classifications.
Create a deployment plan including environment specifications, deployment steps, rollback procedures, and go-live criteria. Include a pilot phase for gradual rollout to minimize risk.
Step 10: Create maintenance strategy
Plan for post-launch support before you build. Define SLAs for different issue types, establish on-call rotations, and document escalation procedures. Create knowledge transfer plans, ensuring the support team understands the system architecture.
Budget for ongoing maintenance. Industry estimates suggest maintenance costs often range from 15-20% of initial development costs annually. Include provisions for security updates, performance optimization, and feature enhancements based on user feedback.
Following this systematic approach transforms complex software development project planning into a manageable process. Each step builds upon the previous, creating a comprehensive plan that significantly increases your project’s success probability.
While these steps provide the framework, understanding the essential components that make up each part of your plan ensures nothing critical gets overlooked.
4 Effective Software Development Plan Templates for Project Managers
Skip the blank page anxiety with these four software development plan templates:
1. Smartsheet- – visual planning for cross-functional teams
Ideal for: Mid-to-large teams needing visual timelines, collaboration, and automation
Smartsheet’s software development plan template includes:
- Pre-built Gantt charts, task dependencies, and timelines
- A structured Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
- Built-in resource planning and risk tracking
Great for project managers who need clear visibility into timelines and team workloads, especially in multi-department setups.
2. Atlassian Confluence – best for agile teams using Jira
Ideal for: Scrum or Kanban teams already using Jira
Confluence’s development planning templates sync with Jira to:
- Auto-update project status as tasks move through workflows
- Include sprint plans, release notes, and technical specs
- Centralize documentation alongside active development
Perfect for dev teams that want planning and execution seamlessly connected.
3. ClickUp – Flexible planning across all methodologies
Ideal for: Teams that switch between Agile, Waterfall, or Hybrid models
ClickUp offers over 10 development-focused templates, including:
- MVP roadmaps, epic tracking, and bug triage boards
- Customizable stages to fit your preferred workflow
- Integrated timelines, docs, and sprint views in one platform
Whether you’re scaling or iterating quickly, ClickUp adapts to your project style.
4. Free Excel/Google Sheets templates
Ideal for: Freelancers, startups, or teams on a budget
Free templates from sites like ProjectManager.com, Vertex42, and Smartsheet offer:
- Simple, tabbed sheets for feature tracking, sprint planning, and QA testing
- Easy sharing and editing in Google Sheets
- No software subscriptions required
Perfect for smaller teams that need structure without a tech stack investment.
With software templates and tools selected, understanding different development methodologies helps you choose the right approach for your project’s unique requirements and constraints.
Selecting the Most Effective Methodology for Project Planning Success
Your software development methodology choice fundamentally shapes how you plan, execute, and deliver software. Here’s how to select the right approach:
1. Agile software development project plan
Agile transforms planning into iterative cycles. Instead of detailed upfront specifications, your agile software development project plan centers on a product backlog with prioritized user stories, 1-4 week sprints, and continuous adaptation based on feedback.
Choose agile software development life cycle when requirements will evolve, you need frequent deliverables, or quick market response matters more than fixed scope.
For example, a mobile app startup would release an MVP in 6 weeks, then iterate based on user feedback every sprint.
2. Waterfall project planning
Waterfall software development follows a linear sequence where each phase completes before the next begins. You’ll document everything upfront: requirements specifications, system design, implementation plans, and testing protocols.
Choose Waterfall for fixed requirements, regulatory compliance projects, or when budget and timeline are non-negotiable.
Government contracts and medical device software often require waterfall’s predictability and comprehensive documentation.
3. Hybrid methodology
According to PMI’s 2024 data, 31.5% of organizations now use hybrid approaches, representing a 57.5% increase from 2020 levels.
Hybrid implementation typically uses:
- Waterfall for infrastructure and architecture phases
- Agile sprints for feature development and UI
- Fixed milestones with flexible execution between gates
A banking app might use waterfall for security infrastructure (fixed requirements) while using agile for customer features (evolving based on feedback).
Now you know what to do. But it’s also important to know what not to do.
Common Mistakes in Software Development Project Planning — and How to Avoid Them
Even well-funded software projects fail when planning missteps go unchecked. By learning from the most common pitfalls, you can proactively safeguard your project’s success. Here are the top 5 mistakes to watch for — and practical strategies to avoid them:
1. Underestimating Project Complexity
It’s a classic trap: tasks appear simpler on paper than they are in practice.
According to Hofstadter’s Law, “It always takes longer than you expect, even when you take into account Hofstadter’s Law.”
How to Avoid It:
- Add a 20–30% time buffer to all major tasks.
- Break down large tasks into subtasks that can be completed within 40 hours or less for better estimation accuracy.
- Use historical data from past projects to inform timelines.
2. Ignoring risk management
Many teams create risk registers at the beginning — and then never revisit them. As a result, critical issues escalate without warning.
How to Avoid It:
- Make risk reviews a standing item in your weekly project meetings.
- Assign clear ownership for each risk.
- Set up trigger conditions that flag when mitigation plans should be activated.
3. Poor Stakeholder Communication
Technical jargon often leads to misalignment with stakeholders, especially when the project’s status isn’t clearly tied to business outcomes.
How to Avoid It:
- Use visual dashboards that map technical progress to business goals.
- Translate updates into tangible milestones, like “Feature X will reduce customer churn by Y%” rather than just “completed sprint 3.”
4. Inadequate Buffer Time:
Planning based solely on “best-case scenarios” leaves no room for unexpected setbacks — like integration issues, scope clarifications, or late-stage bugs.
How to Avoid It:
- Build contingency time into your plan:
- Integration issues: Add ~15% buffer
- Requirement changes: Add ~20% buffer
- Testing & bug fixing: Add ~25% buffer
This keeps the timeline realistic and absorbs common disruptions.
5. Scope Creep Management
What starts as a “small feature” request can spiral into weeks of unplanned work — derailing timelines and resource allocation.
How to Avoid It:
- Establish a formal change control process:
- Log all feature requests
- Assess their impact on scope, time, and budget
- Get written approval before making any changes
From Software Planning to Launch — Space-O Has Got You Covered
Success in software project planning isn’t just about following frameworks; it’s about partnering with teams who’ve mastered the entire process from planning through delivery.
The difference between successful and struggling projects often comes down to systematic planning, clear communication, and experienced execution.
At Space-O Technologies, we’ve delivered over 300 custom software solutions across industries like healthcare, fintech, logistics, and on-demand services. Our planning process goes beyond documentation—we define clear milestones, anticipate risks early, and ensure seamless handoffs between strategy, design, development, and deployment.
Whether you need:
- A step-by-step project plan tailored to your business goals,
- Experienced developers to execute the build,
- Or a full-cycle delivery team to manage everything end-to-end,
we’re here to help you avoid costly delays, scope creep, and budget overruns.
Let’s work together to turn your vision into a successful, scalable software product—built right the first time.
Frequently Asked Questions about Software Development Project Plan
What Is a Software Development Project Plan?
A software development project plan is a comprehensive document outlining how requirements transform into working software. Following established project management standards (originally IEEE 1058-1998, now superseded by ISO/IEC/IEEE 16326:2019), it defines technical and managerial processes necessary for project execution. Think of it as your project’s GPS, providing direction, alternative routes, and delivery timelines.
How long does it take to create a software project plan?
Creating a comprehensive software project plan typically takes 2-4 weeks, depending on project complexity. Simple projects under 3 months might need 5-7 days for planning. Medium complexity projects (3-9 months) require 2-3 weeks. Enterprise projects exceeding 9 months often need 3-4 weeks or more.
Can you create a software project plan in Excel?
Yes, Excel works well for smaller projects. Create tabs for WBS, timeline/Gantt chart, resource allocation, and risk register. Use formulas to calculate budget totals and timeline dependencies. However, Excel becomes unwieldy for teams over 10 people or projects exceeding 6 months.
What’s the biggest mistake in software project planning?
The biggest mistake is planning for best-case scenarios. Teams often estimate assuming no interruptions, perfect communication, and zero technical surprises. This optimism bias causes a majority of project failures. Consider adding buffers based on project complexity. The second biggest mistake? Creating a plan, then never updating it. Successful teams review and adjust plans weekly.
How often should you update a software development project plan?
Update frequency depends on your methodology. Agile teams update sprint plans daily through standups and formally every 1-4 weeks during sprint planning. Waterfall projects need weekly progress updates and formal monthly reviews. All projects should trigger immediate updates when risks materialize, scope changes, or resources shift. Set calendar reminders for regular reviews, and plans gathering dust guarantee project failure.
All our projects are secured by NDA
100% Secure. Zero Spam
*All your data will remain strictly confidential.
Trusted by


Bashar Anabtawi
Canada
“I was mostly happy with the high level of experience and professionalism of the various teams that worked on my project. Not only they clearly understood my exact technical requirements but even suggested better ways in doing them. The Communication tools that were used were excellent and easy. And finally and most importantly, the interaction, follow up and support from the top management was great. Space-O not delivered a high quality product but exceeded my expectations! I would definitely hire them again for future jobs!”

Canada Office
2 County Court Blvd., Suite 400,
Brampton, Ontario L6W 3W8
Phone: +1 (602) 737-0187
Email: sales@spaceo.ca

