
Healthcare App Design: A Complete Guide for Building Better Medical Apps
If you’re building or redesigning a healthcare app, design choices directly affect patient safety, clinician efficiency, and compliance, and working with reputable healthcare app development companies can ensure that the design integrates seamlessly with development milestones.
Poor design leads to errors, missed appointments, and low adoption.
Strong design improves usability, trust, and care outcomes.
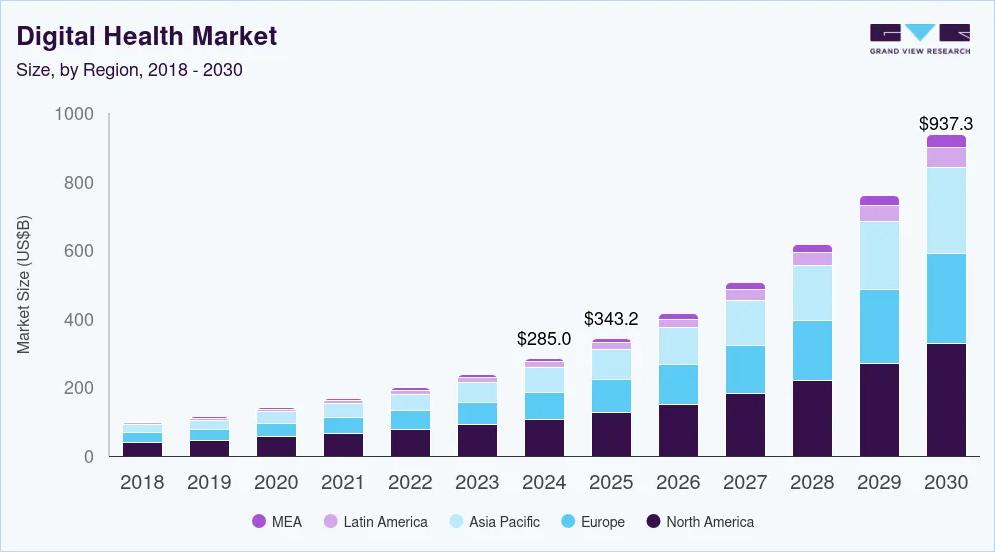
You’re designing for real clinical workflows, not ideal conditions. Your app must be easy to use under pressure, accessible to diverse users, and compliant with healthcare regulations. The numbers prove this matters. According to Grand View Research, the global digital health market reached $211 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at 18.6% annually through 2030.
Space-O Technologies has been designing secure healthcare and enterprise applications since 2018, working with startups, regulated businesses, and Fortune 500 organizations. This guide draws on that experience to explain the principles, compliance requirements, and practical design processes needed to build medical apps that work for both patients and providers.
Here’s what this guide covers:
- Core healthcare app design principles that support patient safety and clinical efficiency
- UI and UX patterns used in patient-facing and clinician-facing medical apps
- Regulatory and compliance considerations, including HIPAA, GDPR, and PIPEDA
- A step-by-step healthcare app design and validation process
- Common design mistakes that reduce adoption or increase compliance risk
- Key cost factors, timelines, and planning considerations for healthcare app projects
What Is Healthcare App Design?
Healthcare app design is the specialized practice of creating digital interfaces for medical applications that serve patients, clinicians, administrators, and other healthcare stakeholders — and professional UI/UX design services ensure usable, compliant experiences across all user groups. It combines user experience design with strict regulatory compliance and clinical workflow requirements, focusing on patient safety, clinical efficiency, and data security in high-stakes environments where mistakes have serious consequences.
How healthcare app design differs from general app design
Healthcare interfaces serve multiple conflicting user needs simultaneously. A retail app optimizes for a single user type, making purchases. Medical apps must work for patients seeking care, doctors reviewing diagnostics, nurses updating records, and administrators managing billing.
The regulatory environment is uniquely complex. Healthcare app ui design must comply with HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA, and FDA guidelines, depending on location and function. These requirements carry legal penalties when violated and must guide design decisions.
Having established what healthcare app design is, the next step is understanding why it demands specialized expertise.
Why Healthcare Apps Require a Unique Design Approach
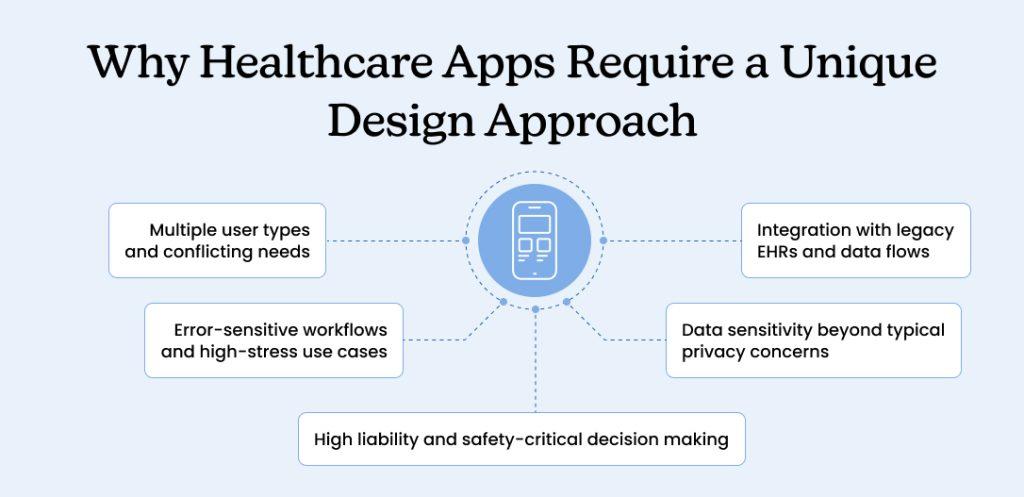
Medical applications operate under constraints that don’t exist in other industries. Understanding these challenges prevents costly mistakes and redesigns.
1. Multiple user types and conflicting needs
Healthcare systems involve patients, physicians, nurses, administrators, insurers, and regulators. Clinicians working with an average of 4-6 digital systems during a single patient encounter need consolidated, fast-loading dashboards. Patients need simplified summaries that avoid medical jargon.
User interface design for healthcare applications must balance these competing priorities through role-based views and customizable displays. A feature that delights patients might frustrate physicians and vice versa.
2. Error-sensitive workflows and high-stress use cases
Medical professionals work under intense time pressure in environments where errors can be fatal. A confusing button placement in a consumer app annoys users. The same issue in a medical app during an emergency could delay treatment.
Healthcare ui design must prevent errors through clear visual hierarchies, confirmation steps for critical actions, and obvious feedback. Color coding, large touch targets, and plain language become essential rather than optional.
3. High liability and safety-critical decision making
Design errors in healthcare apps carry legal and life-threatening consequences. A dosage calculation mistake, missed medication alert, or unclear lab result display can directly harm patients. Every interface decision requires evidence-based justification and exhaustive testing.
Medical app design requires defensive design patterns that assume users are distracted, tired, and working under pressure. Alert fatigue from too many notifications causes clinicians to ignore critical warnings.
4. Data sensitivity beyond typical privacy concerns
Healthcare data reveals intimate details about physical health, mental state, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle choices. Breaches expose information that can’t be changed like passwords. Design must balance data access with privacy protection.
Clinicians need comprehensive patient histories during emergencies but shouldn’t access records inappropriately. The interface must make appropriate access easy and inappropriate access difficult without creating friction.
5. Integration with legacy EHRs and data flows
Most healthcare organizations run on decades-old electronic health record systems that weren’t designed for modern integration. Medical app ui design must bridge these legacy platforms with contemporary user experiences.
Data must flow seamlessly between new apps and existing clinical systems. Duplicate data entry wastes time and introduces errors. Real-time sync ensures providers see current information regardless of which system they’re using.
Space-O Technologies specializes in healthcare software modernization that connects modern interfaces to legacy backend systems without disrupting clinical operations.
4 Core UI/UX Principles and Patterns for Healthcare App Design
Effective medical interfaces follow proven patterns that improve usability and reduce errors across diverse user populations.
1. Simple navigation and clear information hierarchy
Healthcare apps handle complex information that must be accessible quickly. Simple navigation uses familiar patterns, including tabs for major sections, clear back buttons, and logical grouping of related functions. Critical information appears first, with details available through progressive disclosure.
Patients should reach appointment booking, medication lists, and test results in three taps or fewer from the home screen. Use consistent placement for recurring elements. Search always appears in the same location. Log out stays in the same menu position.
2. Accessibility and inclusive design
Healthcare serves everyone, including people with disabilities. Accessibility is not optional but legally required under WCAG 2.1 guidelines. Color contrast ratios must meet 4.5:1 minimum for normal text and 3:1 for large text. All functions must work with screen readers, keyboard navigation, and voice commands.
Design for aging eyes with larger fonts, clear icons, and ample white space. Support multiple languages for diverse patient populations. Test designs with actual patients who have disabilities rather than assuming compliance through technical audits alone.
3. Trust-building through clear interactions and transparency
Medical apps handle extremely sensitive personal information. Users need to trust that their data is secure and used appropriately. Health app ui design builds trust through transparent privacy controls, clear consent processes, and obvious security indicators.
Show users exactly what data you’re collecting, why you need it, and who can access it. Make privacy settings easy to find and adjust. Use plain language to explain complex data practices.
Provide clear feedback for every action. When a prescription refill is requested, confirm it’s received and show the expected processing time. When test results arrive, notify users promptly. Uncertainty creates anxiety, so clear status updates build confidence.
4. Error prevention and validation
Healthcare apps must prevent errors before they happen. Wrong patient selection, incorrect dosage calculations, and missed allergy warnings can cause serious harm. Design patterns like confirmation dialogs, visual verification, and constraint-based inputs reduce human error.
Use clear error states that explain what went wrong and how to fix it. Color-code critical actions like “delete” or “confirm treatment” with additional verification steps. Validation should happen in real-time, alerting users immediately when data conflicts with patient records or clinical guidelines.
Applying core principles: UI design dos and don’ts
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Use large fonts (16pt+ for body text) | Cram dense text blocks |
| Provide clear action buttons with color coding | Use ambiguous generic buttons |
| Show progress indicators for multi-step tasks | Leave users guessing about process length |
| Use icons with text labels | Rely on icons alone without labels |
| Provide contextual help and tooltips | Assume users know medical terminology |
Pro Tip: Use progressive disclosure to reduce cognitive load for clinicians handling high-stress workflows. Show essential information first with expandable sections for comprehensive details.
Space-O Technologies documents emerging trends that apply specifically to healthcare contexts. Learn more about mobile app UI/UX design trends shaping medical interfaces.
With core design principles established, understanding compliance requirements becomes essential for implementation.
3 Compliance-Focused Design Requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA)
Regulatory compliance shapes every aspect of healthcare mobile app design from authentication flows to data storage decisions.
1. Secure authentication and privacy-aware flows
HIPAA requires secure methods to verify user identity before granting access to protected health information. Two-factor authentication (2FA) should be standard, not optional. Biometric options like fingerprint or face recognition provide convenience without sacrificing security.
Session timeouts prevent unauthorized access when devices are left unattended. Automatic logout after 15-30 minutes of inactivity is common. Privacy-aware design shows only necessary information at each step. Mask sensitive data by default with options to reveal when needed.
2. Data minimization and consent patterns
GDPR and PIPEDA require collecting only data that’s necessary for stated purposes. Healthcare ui design must include granular consent controls, letting users choose what they share. Pre-checked consent boxes don’t meet legal standards because users must actively opt in.
Consent language must be clear and specific. Specify exactly which third parties, for what purposes, and give users control over each category. Allow users to export their data in standard formats and request deletion where legally permitted.
3. Audit trails and logging
HIPAA requires comprehensive audit logs showing who accessed what data and when. Healthcare user interface design for healthcare applications must accommodate these logging requirements without impacting performance or usability.
Administrators need dashboards showing unusual access patterns, failed login attempts, and data exports. Clear reports help organizations demonstrate compliance during regulatory audits.
3 Compliance-Focused Design Requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, PIPEDA)
Regulatory compliance shapes every aspect of healthcare mobile app design from authentication flows to data storage decisions.
1. Secure authentication and privacy-aware flows
HIPAA requires secure methods to verify user identity before granting access to protected health information. Two-factor authentication (2FA) should be standard, not optional. Biometric options like fingerprint or face recognition provide convenience without sacrificing security.
Session timeouts prevent unauthorized access when devices are left unattended. Automatic logout after 15-30 minutes of inactivity is common. Privacy-aware design shows only necessary information at each step. Mask sensitive data by default with options to reveal when needed.
2. Data minimization and consent patterns
GDPR and PIPEDA require collecting only data that’s necessary for stated purposes. Healthcare ui design must include granular consent controls, letting users choose what they share. Pre-checked consent boxes don’t meet legal standards because users must actively opt in.
Consent language must be clear and specific. Specify exactly which third parties, for what purposes, and give users control over each category. Allow users to export their data in standard formats and request deletion where legally permitted.
3. Audit trails and logging
HIPAA requires comprehensive audit logs showing who accessed what data and when. Healthcare user interface design for healthcare applications must accommodate these logging requirements without impacting performance or usability.
Administrators need dashboards showing unusual access patterns, failed login attempts, and data exports. Clear reports help organizations demonstrate compliance during regulatory audits.
Compliance Requirements by Standard
| Standard | Applies To | UI Design Impact |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA | US healthcare data | 2FA, session timeouts, access controls, audit logs |
| GDPR | EU personal data | Granular consent, data export, right to erasure |
| PIPEDA | Canadian personal data | Consent for collection/use, data portability, transparency |
Canada’s PIPEDA requires organizations to obtain meaningful consent before collecting personal information. This means healthcare web app design services must include clear, understandable consent processes specifically tailored for Canadian users.
Space-O Technologies follows web application security best practices that exceed minimum compliance requirements.
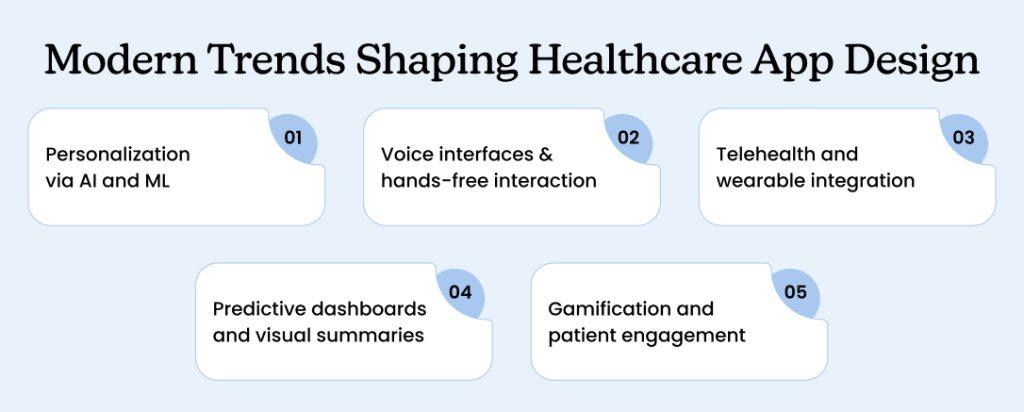
5 Modern Trends Shaping Healthcare App Design
Modern innovations are reshaping how medical interfaces work and what users expect from healthcare apps — and a variety of healthcare app ideas can spark your strategy for meaningful functionality.
1. Personalization via AI and ML
Artificial intelligence customizes healthcare experiences based on individual user data, preferences, and medical history — and exploring real-world use cases of OpenAI in healthcare industry illustrates how AI transforms patient engagement and clinical insights.
AI-powered apps suggest relevant health content, predict medication adherence issues, and flag abnormal patterns in self-reported symptoms.
The key is transparent data use. Patients need to understand what data trains AI models and how predictions are generated. Safety controls are critical – AI suggestions should support clinical decisions rather than replace professional judgment. Any diagnostic or treatment suggestions generated by AI require human clinical oversight before implementation.
2. Voice interfaces and hands-free interaction
Voice technology enables hands-free documentation and patient interaction, particularly valuable for clinicians managing multiple tasks simultaneously. Physicians can dictate notes without touching keyboards. Patients with limited mobility or vision impairments can navigate apps using natural language commands.
Designing conversational interfaces requires different thinking than visual UI. Interactions must feel natural and forgiving. Error handling needs to be robust since voice recognition isn’t perfect in noisy clinical environments.
3. Telehealth and wearable integration
Telehealth moved from experimental to essential during the pandemic and continues growing. Modern healthcare app ui design examples embed video consultations directly into apps rather than redirecting to separate platforms. Patients book appointments, join video visits, and access visit summaries all in one interface.
Wearable devices generate continuous health data from smartwatches and fitness trackers. Well-designed apps surface meaningful patterns from this data without overwhelming users with raw numbers. Integration requires standardized data formats and secure APIs.
4. Predictive dashboards and visual summaries
AI analyzes patient data to predict health risks before problems become acute. Predictive dashboards alert clinicians to patients at high risk for hospital readmission, medication non-adherence, or disease progression. Recent healthcare IT surveys report widespread adoption of predictive analytics across health systems.
Visual summaries condense complex medical data into scannable formats. Timeline views show medication history. Risk scores communicate the likelihood of complications. Use clear, calibrated language and avoid false precision.
5. Gamification and patient engagement
Game design elements improve patient engagement and adherence, particularly for chronic disease management. Points, badges, progress tracking, and challenges make managing conditions less burdensome and more motivating. Apps turn diabetes management or cardiac rehabilitation into achievable daily quests.The key is authentic gamification that serves health goals rather than superficial point systems. Balance fun with clinical validity. Space-O Technologies builds healthcare app development solutions that incorporate proven engagement strategies while maintaining medical accuracy.
Plan a Compliant, User-Friendly Healthcare App?
Get expert guidance on UX, compliance, and patient-centric workflows for your healthcare mobile application.
Space-O Technologies stays current with trends in mobile app development while maintaining focus on proven, reliable solutions.
Understanding trends informs strategy, but execution requires a structured design process.
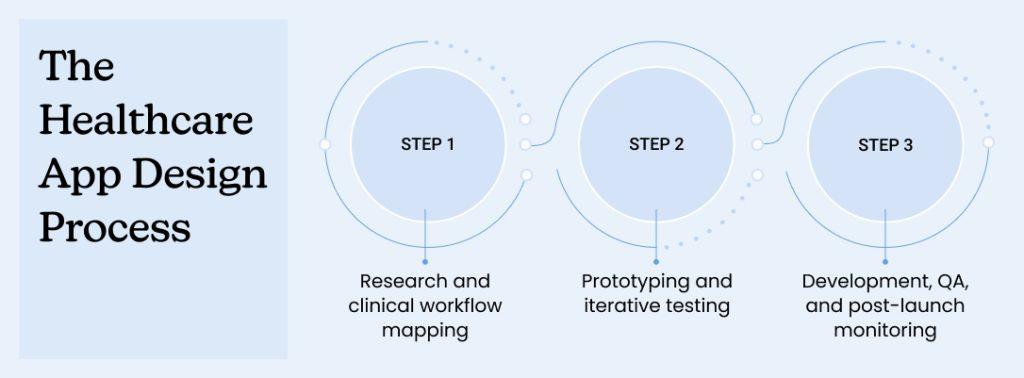
The Healthcare App Design Process in 3 Steps
Creating effective healthcare apps requires a structured approach that validates decisions at each phase.
Step 1: Research and clinical workflow mapping
Start with extensive user research across all stakeholder groups. Shadow physicians during typical workdays to understand their actual workflows, pain points, and time pressures. Interview patients about their experiences with existing healthcare apps and what frustrates them.
Map existing clinical workflows in detail before designing digital versions. Document every step, decision point, and handoff between roles. Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies that better design could eliminate.
Create detailed personas representing each user type, including goals, technical comfort levels, and primary use contexts. Reference these personas throughout the design process to ensure every decision serves real user needs.
Deliverables in this step: User research report, workflow maps, stakeholder personas, requirements document
Step 2: Prototyping and iterative testing
Begin with low-fidelity wireframes, exploring different layout approaches and navigation structures. An MVP app development approach helps validate core interactions before full-scale design builds.
Test these rough concepts with representative users to validate basic approaches before investing in detailed design.
Create medium-fidelity prototypes, adding interaction patterns, content hierarchy, and information architecture. Using the right mobile app design tools accelerates iteration and improves fidelity. Test again with users attempting realistic tasks. Observe where they hesitate, what confuses them, and what delights them.
Develop high-fidelity mockups only after validating core interactions. Include final visual design, typography, colors, and detailed interactions. Create interactive prototypes that simulate the complete user experience for comprehensive usability testing.
Test accessibility at each fidelity level using both automated tools and manual evaluation. Recruit test participants with disabilities to reveal usability issues that technical audits miss.
Deliverables in this step: Wireframes, interactive prototypes, usability test reports, accessibility audit, design system documentation
Pro Tip: Validate prototypes with at least one clinician and one non-technical patient to avoid biased usability results. These groups have fundamentally different needs that both must be satisfied.
Step 3: Development, QA, and post-launch monitoring
During the mobile app development process, provide developers with comprehensive design specifications, including measurements, color values, font sizes, and interaction details — and consider hiring expert app developers to ensure pixel-perfect implementation. A detailed design system ensures consistent implementation across the entire application.
Conduct QA testing focused on design fidelity, ensuring the implemented app matches approved designs. Test across devices, screen sizes, and operating system versions to verify responsive behavior and consistent appearance.
Monitor usage after launch through analytics, heat maps, and user feedback channels. Track key metrics including task completion rates, time-on-task, error rates, and abandonment points. This data guides iterative improvements based on real-world usage patterns.
Schedule design reviews three and six months post-launch to assess what’s working and what needs refinement. Custom healthcare app design and development is an ongoing process rather than a one-time project.
Deliverables in this step: Design specifications, QA reports, analytics dashboards, post-launch optimization recommendations
3 Common Design Mistakes and How to Validate Your Healthcare App UX
Even experienced designers make predictable mistakes when creating medical interfaces. Here’s how to recognize and avoid these patterns.
Common UX Mistakes and Solutions
| Mistake | Impact | Quick Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Overloaded dashboards | Users miss critical info | Single-focus screens with progressive disclosure |
| Medical jargon for patients | Reduced comprehension and trust | Plain language with optional tooltips for details |
| Skipping edge-case design | App breaks in real scenarios | Map error states and offline modes |
| No onboarding | Users don’t discover features | Interactive tutorials at first launch |
Pro Tip: Record usability sessions to capture subtle user hesitations that written feedback often misses. Body language and micro-expressions reveal confusion before users articulate problems.
Let’s understand each mistake in detail.
Mistake 1: Overloaded dashboards and complex language
Cramming too much information onto single screens overwhelms users and hides critical data in visual noise. Medical jargon alienates patients who lack clinical training. A physician understands “hypertension” and “myocardial infarction” but patients need “high blood pressure” and “heart attack.”
How to avoid it: Focus dashboards on specific tasks or user goals rather than displaying everything available. User interface design for healthcare applications requires plain language for patient-facing content while supporting clinical terminology where professionals expect it. Test readability using standard metrics – patient-facing content should score at 8th-grade reading level or below.
Mistake 2: Poor onboarding and missing edge-case handling
New users need guidance understanding what the app does and how to accomplish common tasks. Many apps fail to design for edge cases including interrupted processes, network failures, and incomplete data. What happens when a video consultation drops mid-appointment?
How to avoid it: Highlight key features through interactive tutorials or contextual tips at relevant moments. Design for common edge cases in healthcare contexts – delayed lab results, dropped video calls, incomplete patient data. Error messages must be helpful rather than technical. “Network connection lost, trying to reconnect” is better than “Error 503.”
Mistake 3: Skipping formal usability validation
Assuming designs work without testing with real users leads to interfaces that fail in production. Internal reviews miss problems that actual patients and clinicians encounter under real-world conditions.
How to avoid it: Conduct formal usability testing with 5-8 users per stakeholder group. Assign realistic tasks and observe completion rates, time-on-task, and errors. Use heatmaps to reveal which interface elements get noticed and which are ignored. Apply System Usability Scale (SUS) for quantitative benchmarking – scores below 60 indicate significant problems requiring redesign.
Space-O Technologies uses comprehensive software testing checklists that include usability validation at multiple project phases.
What Does Healthcare App Design Cost? Key Factors and Ranges
Understanding cost factors helps organizations plan realistic budgets and set appropriate expectations for healthcare app projects — and reviewing healthcare app development cost benchmarks can sharpen your financial planning.
Healthcare mobile app design services typically range from $50,000 for simple applications to $300,000+ for enterprise-grade platforms with complex requirements. Several factors significantly impact final costs:
Healthcare App Design Cost Ranges
| Project Complexity | Typical Cost Range | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Simple patient portal | $50,000 – $100,000 | 3-4 months |
| Medium platform with integrations | $100,000 – $250,000 | 6-9 months |
| Complex enterprise system | $250,000 – $500,000+ | 9-15 months |
Primary cost drivers: Application scope and features, compliance requirements, legacy system integration, development timelines, AI/ML capabilities, wearable device integration, and enterprise-grade security measures.
These ranges reflect Toronto market rates and assume clean requirements, available stakeholders, and minimal scope changes during development.
6 Key Factors Impacting App Design Cost
1. Application scope and feature complexity
Application scope dominates cost variation. A basic patient portal with appointment scheduling and secure messaging costs significantly less than a comprehensive telemedicine platform with video consultations, AI diagnostics, and real-time EHR integration.
The number of user roles, features, and platforms (iOS, Android, web) directly impacts development time and cost. Each additional feature requires design, development, testing, and maintenance.
2. Compliance and security requirements
Compliance requirements add substantial design and development time. HIPAA-compliant apps need extensive security audits, penetration testing, and documentation. Multi-jurisdiction support covering the US, Canada, and EU requirements multiplies compliance work.
Security measures, including encryption, audit logging, and access controls, require specialized expertise. Regulatory reviews can extend timelines by 2-6 months, depending on FDA involvement and medical device classification.
3. Legacy system integration
Legacy system integration represents a major variable cost. Connecting to modern EHR platforms via standard APIs is straightforward. Integrating with decades-old proprietary systems requires custom development that’s difficult to estimate accurately.
Data migration, real-time sync, and maintaining compatibility with existing workflows add complexity. Each hospital or clinic may use different EHR systems requiring separate integration work.
4. Development timelines and milestones
Simple healthcare apps take 3-4 months from concept to launch. This includes 3-4 weeks for research and design, 6-8 weeks for development, and 2-3 weeks for testing and deployment.
Complex healthcare platforms require 6-12 months or more.
Timeline factors include:
- Requirements gathering and user research: 4-6 weeks
- Design and prototyping: 6-10 weeks
- Development and integration: 12-24 weeks
- Compliance review and security testing: 4-8 weeks
- User acceptance testing and deployment: 3-4 weeks
5. AI, ML, and advanced analytics
AI and machine learning features significantly increase costs. Developing, training, and validating AI models requires data science expertise beyond standard app development. Ongoing model maintenance and monitoring add recurring costs.
Predictive analytics, natural language processing, and computer vision require specialized technical skills and infrastructure. Model accuracy must meet clinical validation standards.
6. Wearable device and IoT integration
Wearable device integration needs specialized development for each platform, including Apple HealthKit, Google Fit, and Fitbit SDK. Supporting multiple devices and handling data inconsistencies across platforms increases complexity.
Real-time data processing, battery optimization, and Bluetooth connectivity require additional technical considerations. Each device manufacturer may have different APIs and data formats.
Examples of Effective Healthcare App Design
These examples illustrate how design principles translate into successful applications:
Example 1:
A mid-sized hospital network redesigned its patient portal to reduce the number of steps to book an appointment from 7 to 3. The new interface starts with a clear question: “What do you need today?” Options include Schedule Appointment, Message Provider, View Results, and Refill Prescription.
Appointment booking shows available slots immediately based on the user’s preferred provider and location, no separate search required. Confirmation happens on a single screen with calendar integration and automatic reminders.
Result: Appointment booking completion rate increased significantly. Phone calls to scheduling staff decreased substantially.
Example 2:
A chronic disease management app consolidates data from glucose monitors, blood pressure cuffs, and activity trackers into a single patient dashboard. Visual trends show whether conditions are improving or worsening over weeks and months.
The clinician’s view prioritizes patients requiring attention. Color-coded alerts highlight abnormal readings and patients overdue for check-ins. Physicians can review patient data and send messages without switching between multiple systems.
Result: Hospital readmission rates for chronic condition patients decreased significantly. Clinician time spent reviewing remote monitoring data improved through better prioritization.
Example 3:
A telehealth startup designed its entire experience for smartphones rather than adapting a desktop interface. Large touch targets accommodate users with limited dexterity. Clear visual indicators show connection quality and recording status.
The pre-visit screen collects chief complaint and current symptoms using simple forms with photo/video upload options. During visits, patients can share their screen to show rashes or injuries. Visit summaries arrive via text message with next steps in plain language.
Result: Most appointments completed successfully on the first attempt. Patient satisfaction scores remained consistently high, with particular praise for ease of use.
These examples demonstrate medical app UI patterns that solve real problems through thoughtful attention to user needs and workflows.
Start Your Healthcare App Design Project with Space-O
Start Your healthcare app design project with Space-O — from strategy to execution, our healthcare app development services cover UI/UX design, prototyping, compliance, and full-scale deployment.
Space-O Technologies specializes in designing intuitive healthcare interfaces that balance complex medical UI design requirements with exceptional user experiences. Since 2018, we’ve partnered with healthcare providers, medical technology companies, and digital health startups to create compliant, user-centered designs.
Our healthcare app design expertise includes:
- User research and clinical workflow mapping across all stakeholder groups
- HIPAA, GDPR, and PIPEDA-compliant interface design
- Accessibility-first design meeting WCAG 2.1 standards
- Role-based UI for patients, clinicians, and administrators
- Interactive prototyping and iterative usability testing
- Design systems and comprehensive UI specifications
What our healthcare clients say:
Space-O didn’t just develop an app; they created a meaningful tool that supports better health outcomes. The team’s project management is excellent. The team has impressive technical expertise, has delivered on time, and is responsive to the client’s questions.
– Duane Mancini, M. Sc., CEO, Project Medtech
Trusted by 100+ clients with a 65% repeat business rate, Space-O delivers healthcare UX design and end-to-end development support. We work closely with your clinicians and IT teams throughout the design process to ensure interfaces improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Whether you’re building a new telemedicine platform, modernizing a patient portal, or creating specialized clinical tools, our design team brings proven expertise in medical app UI/UX that meets both user needs and regulatory requirements.Connect with experienced app developers in Toronto who understand healthcare’s unique design challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions about Healthcare App Design
What’s the difference between patient-facing and clinician-facing healthcare app design?
Patient-facing apps prioritize simplicity and plain language. Clinician apps need information density and speed. A patient portal shows “Your blood pressure is high” while clinician dashboards display detailed vitals, trends, and histories. Most platforms require both interfaces with role-based switching.
Should I start with iOS, Android, or web for my healthcare app?
For clinical staff, web works best on hospital desktops and tablets. For patients, choose iOS for higher-income markets or Android for broader reach. Cross-platform frameworks like React Native serve both platforms, but may compromise platform-specific features like HealthKit integration.
How to choose between custom design and healthcare UI templates
Templates accelerate development but create generic experiences. Custom designs cost 30-50% more than templates, but differentiate your brand. Use templates for MVPs or internal tools. Invest in custom design when patient experience is your competitive advantage or when workflows are highly specialized.
What’s the biggest mistake startups make when designing healthcare apps?
Designing for themselves rather than actual users. Founders create interfaces they’d want instead of what stressed patients or time-pressed clinicians need. The second mistake is treating HIPAA/GDPR as an afterthought. Both lead to expensive redesigns. Involve real users from day one.
Do I need FDA approval for my healthcare app design?
It depends on function, not design. Apps that diagnose, treat, or prevent disease typically require FDA clearance. Wellness apps, portals, and EHR interfaces usually don’t. Consult FDA guidance early or work with regulatory consultants to determine your classification before designing.
All our projects are secured by NDA
100% Secure. Zero Spam
*All your data will remain strictly confidential.
Trusted by


Bashar Anabtawi
Canada
“I was mostly happy with the high level of experience and professionalism of the various teams that worked on my project. Not only they clearly understood my exact technical requirements but even suggested better ways in doing them. The Communication tools that were used were excellent and easy. And finally and most importantly, the interaction, follow up and support from the top management was great. Space-O not delivered a high quality product but exceeded my expectations! I would definitely hire them again for future jobs!”

Canada Office
2 County Court Blvd., Suite 400,
Brampton, Ontario L6W 3W8
Phone: +1 (602) 737-0187
Email: sales@spaceo.ca

